* Sums of Discrete Random Variable
- Convolution
X,Y : two independent discrete R.V. with distribution functions m(x) and m(y) (Ω : Integer)
r.v. Z = X+Y.

이 때, Z의 distribution은 X=k 라고 두고 m(z) = P(Z=z) = sum(P(X=k)P(Y=z-k)) {X=0~k} 로 구할 수 있다.
따라서 X,Y가 2개의 independent discrete r.v.s 이며 m1(x), m2(y)를 가진다고 하였을 때,
m1(x), m2(y)의 convolution인 distribution function m3(z) = m1(x)*m2(y)는 다음과 같이 정의된다.

같은 식으로 접근하면 S(n) = X1~Xn의 합일 때 S(n) = S(n-1) + Xn 이므로 Sn의 distribution function은 다음과 같이 정의될 수 있다.

Ex)
한 개의 주사위를 2번 굴릴 때, 그 결과를 X1,X2 라고 하자. 이때 r.v. S2 = X1+X2로 정의된다.
S2의 Distribution function 은?
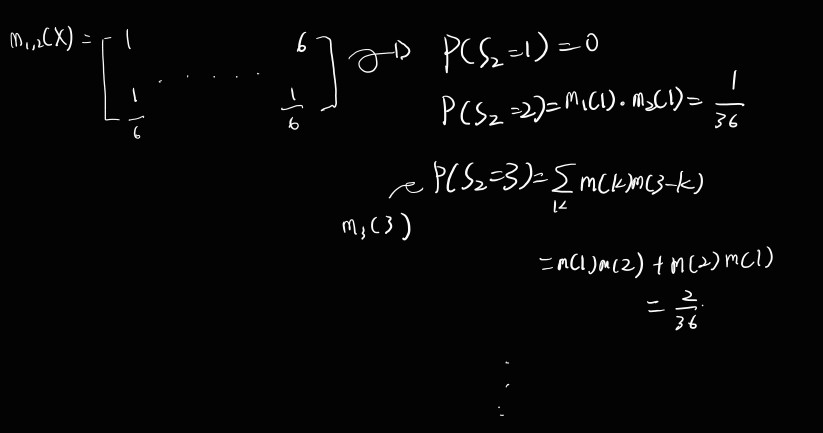
만약 S3 = X1+X2+X3 와 같이 주어졌다면,
P(S3=3) = m2(k)m(3-k) = P(S2=2)*m(1) = 1/216 과 같이 구할 수 있다.
- Sums of continuous Random Variables
X,Y : Conti r.v. with density functions f(x) and g(y)
=> f,g의 convolution은 다음과 같이 정리된다.

X,Y가 독립이며 fx(x), fy(y)를 가진다면, Z=X+Y의 density function fz는
fz(z) = fx*fy로 나타낼 수있다.
* Sum of two independent Uniform Random Variables
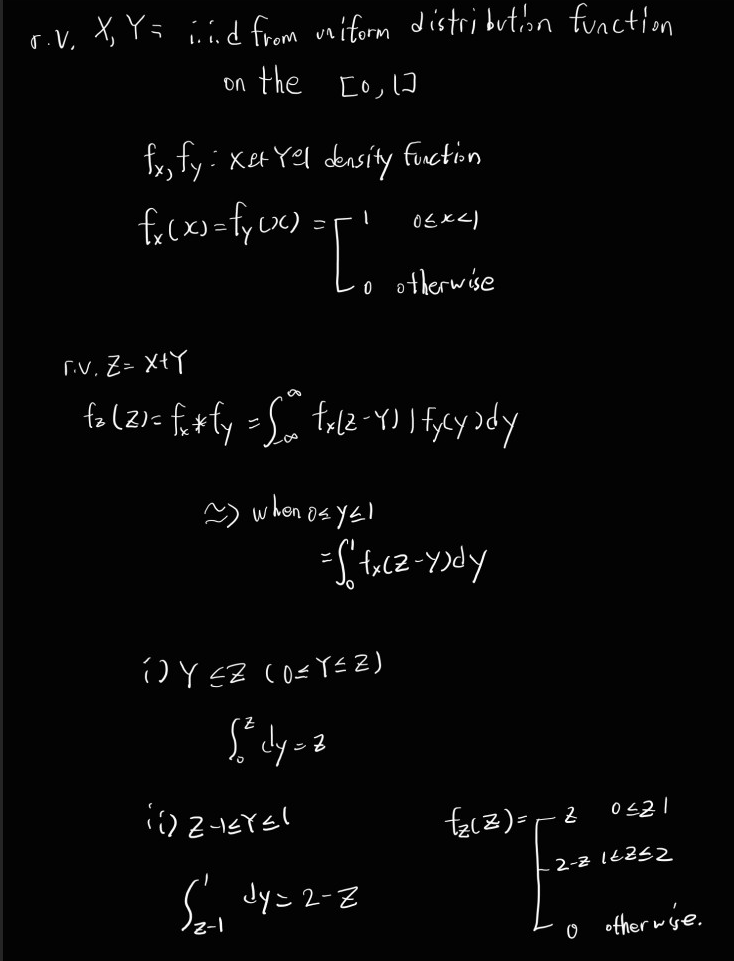
(0<z<1, 1<=z<=2로 나눈다.)
* Sum of two exponential Rnadom Variables
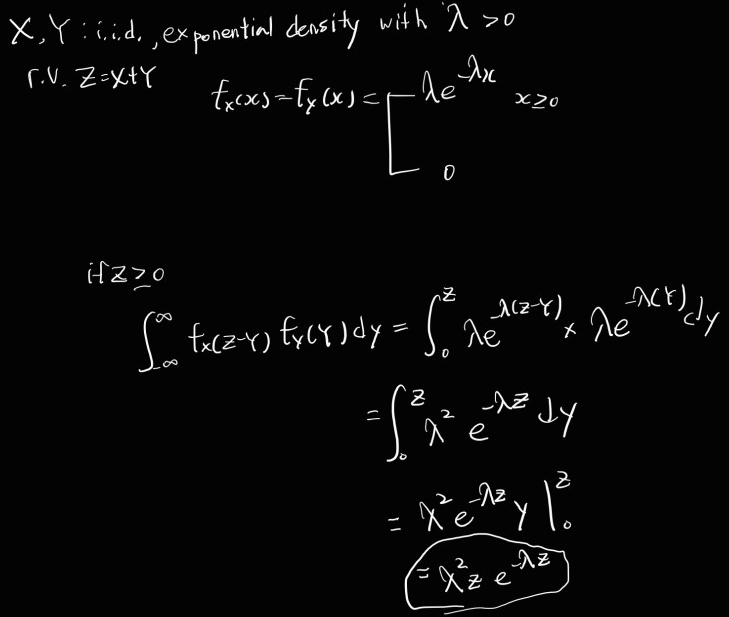
* chi-squared density(X^2)
degree of freedom이 m일 경우

* Gamma function


(observed - n*m(x))^2 / n*m(x)일 때, V는 자유도가 n-1인 chi-distribution을 지닌다.
* r.v. X1,X2,X3...Xi가 i.i.d.이면서 Sn=X1+X2+...+Xn일 때 fsn(x)=(fx1*fx2*fx2*...*fxn)(x)이다.
ex)
roll a die
=>
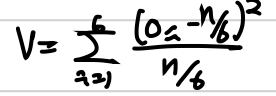
=> 자유도가 5인 chi density function을 지닌다.
ex)
r.v. Xi 가 [0,1]사이에서 uniformly distributed fkaus, Sn = X1+X2+X3+...일 때,

ex) Xi가 exponential 이라면,
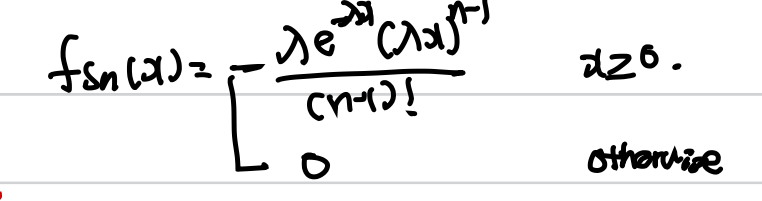
ex) Xi가 표준 정규 분포를 따른다면,

'개인 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 확률 및 통계 - 9. Central Limit Theorem (CLT) (0) | 2024.05.23 |
|---|---|
| 확률 및 통계 - 8. Law of Large Number (0) | 2024.05.07 |
| 데이터 과학 - 12. Clustering Part 2(DBScan) (0) | 2024.04.27 |
| 데이터 과학 - 11. Clustering (0) | 2024.04.25 |
| 데이터 과학 - 10. Association Rule Mining (0) | 2024.04.24 |